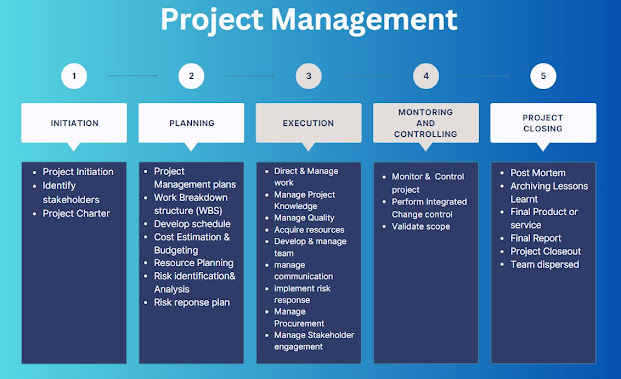
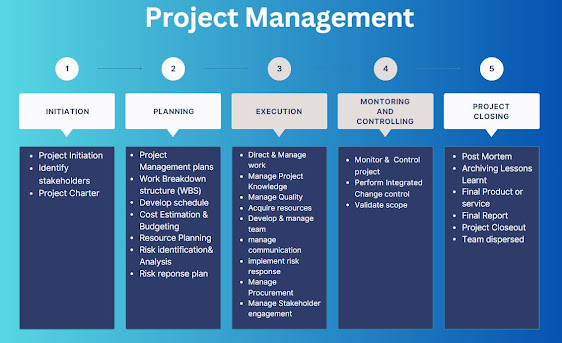
Stakeholder Management is the process of identifying, analyzing, and engaging with stakeholders to ensure that their needs and expectations are considered in the decision-making process.
Stakeholders are individuals or groups that have an interest in or are affected by an organization's activities, projects, or initiatives.
Effective stakeholder management is crucial for the success of any organization as it helps to build trust, manage risks, and achieve the desired outcomes.
In this article, we will explore the key aspects of stakeholder management, the benefits of effective stakeholder management, and some best practices.
Key Aspects of Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management typically involves the following key aspects:
- Identification: The first step in stakeholder management is to identify all stakeholders who have an interest in or are affected by an organization's activities, projects, or initiatives. This may include customers, employees, suppliers, shareholders, government agencies, community groups, and others.
- Analysis: Once stakeholders have been identified, their needs and expectations must be analyzed to determine the level of interest and influence they have on the organization's activities. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gather information about their concerns, opinions, and preferences.
- Engagement: The next step is to engage with stakeholders to ensure that their needs and expectations are considered in the decision-making process. This may involve providing regular updates, soliciting feedback, and involving stakeholders in the planning and implementation process.
- Monitoring: Finally, stakeholder engagement must be monitored and evaluated to ensure that stakeholders are satisfied with the outcomes and that their needs and expectations are being met.
Benefits of Effective Stakeholder Management
Effective stakeholder management provides numerous benefits for organizations, including:
- Improved Decision Making: Effective stakeholder management can help organizations to make more informed decisions by taking into account the perspectives and interests of all stakeholders.
- Risk Mitigation: Stakeholder management can help organizations to identify and mitigate risks by anticipating potential issues and addressing them proactively.
- Reputation Management: Effective stakeholder management can help organizations to build and maintain a positive reputation by engaging with stakeholders in a transparent and responsible manner.
- Increased Support: By engaging with stakeholders and addressing their needs and expectations, organizations can gain the support and buy-in of stakeholders, which can be crucial for the success of projects and initiatives.
Best Practices in Stakeholder Management
Some best practices in stakeholder management include:
- Stakeholder Mapping: Organizations should develop a stakeholder map that identifies all stakeholders, their level of interest, and influence on the organization's activities.
- Regular Communication: Organizations should provide regular updates to stakeholders, solicit feedback, and involve them in the decision-making process.
- Transparency: Organizations should be transparent in their communication with stakeholders, providing accurate and timely information about their activities, projects, and initiatives.
- Customization: Organizations should tailor their communication and engagement strategies to the specific needs and expectations of different stakeholder groups.
- Evaluation: Organizations should regularly evaluate their stakeholder engagement activities to ensure that they are effective and that stakeholders' needs and expectations are being met.
Conclusion
Effective stakeholder management is essential for the success of any organization as it helps to build trust, manage risks, and achieve the desired outcomes.
Stakeholder management involves identifying, analyzing, engaging with, and monitoring stakeholders to ensure that their needs and expectations are considered in the decision-making process.
By implementing best practices in stakeholder management, organizations can make more informed decisions, mitigate risks, build a positive reputation, and gain the support of stakeholders.